Monday, April 11, 2022
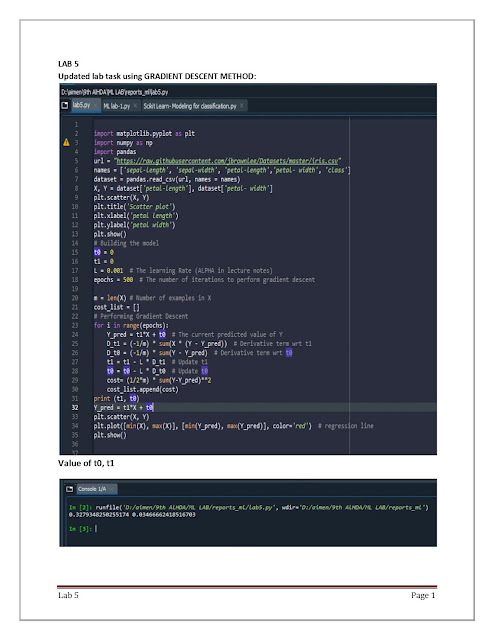
Linear Regression Gradient descent method
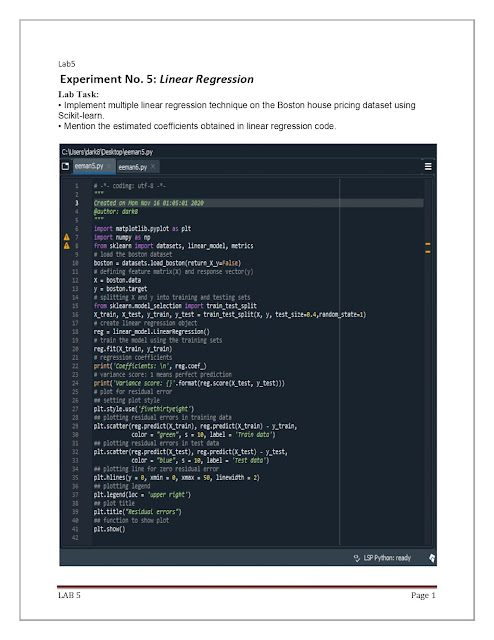
Implement multiple linear regression techniques on the Boston house pricing dataset using Scikit-learn.
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import pandas
url = “https://raw.githubusercontent.com/jbrownlee/Datasets/master/iris.csv"
names = [‘sepal-length’, ‘sepal-width’, ‘petal-length’,’petal- width’, ‘class’]
dataset = pandas.read_csv(url, names = names)
X, Y = dataset[‘petal-length’], dataset[‘petal- width’]
plt.scatter(X, Y)
plt.title(‘Scatter plot’)
plt.xlabel(‘petal length’)
plt.ylabel(‘petal width’)
plt.show()
# Building the model
t0 = 0
t1 = 0
L = 0.001 # The learning Rate (ALPHA in lecture notes)
epochs = 500 # The number of iterations to perform gradient descent
m = len(X) # Number of examples in X
cost_list = []
# Performing Gradient Descent
for i in range(epochs):
Y_pred = t1*X + t0 # The current predicted value of Y
D_t1 = (-1/m) * sum(X * (Y — Y_pred)) # Derivative term wrt t1
D_t0 = (-1/m) * sum(Y — Y_pred) # Derivative term wrt t0
t1 = t1 — L * D_t1 # Update t1
t0 = t0 — L * D_t0 # Update t0
cost= (1/2*m) * sum(Y-Y_pred)**2
cost_list.append(cost)
print (t1, t0)
Y_pred = t1*X + t0
plt.scatter(X, Y)
plt.plot([min(X), max(X)], [min(Y_pred), max(Y_pred)], color=’red’) #regression line
plt.show()
Output:
plt.plot(list(range(epochs)), cost_list, ‘-r’) #plot the cost function.
Implement KNN
Implement KNN on any data set and choose different values of K to see how it impacts the accuracy of the predictions.
Quadratic Discriminant Analysis in PYTHON
Implement QDA on any dataset and explain with comments. Each student should implement on different dataset.
Dataset: Breast cancer
Sunday, April 10, 2022
Scikit-Learn | PCA
Implementing PCA in Python with Scikit-Learn on Iris dataset.
Step 01: importing required libraries
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import pandas as pd
from sklearn import datasets
Step 02: importing or loading the datasets
dataset = datasets.load_iris()
Step 03: distributing the dataset into two components X and Y
X = dataset.data ; y = dataset.target
Step 04: Splitting the X and Y into the Training set and Testing set
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size = 0.25, random_state = 75)
Step 05: performing preprocessing part
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
sc = StandardScaler()
X_train = sc.fit_transform(X_train)
X_test = sc.transform(X_test)
Step 06: Applying PCA function on training and testing set of X component
from sklearn.decomposition import PCA
pca = PCA(n_components = 2)
X_train = pca.fit_transform(X_train)
X_test = pca.transform(X_test)
Step 07: Fitting Logistic Regression To the training set
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
classifier = LogisticRegression(random_state = 0)
classifier.fit(X_train, y_train)
Step 08: Predicting the test set result using predict function under LogisticRegression
y_pred = classifier.predict(X_test)
Step 09: making confusion matrix between test set of Y and predicted value.
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix
cm = confusion_matrix(y_test, y_pred)
Step 10: Predicting the training set result through scatter plot
from matplotlib.colors import ListedColormap
X_set, y_set = X_train, y_train
X1, X2 = np.meshgrid(np.arange(start = X_set[:, 0].min() — 1,
stop = X_set[:, 0].max() + 1, step = 0.01),
np.arange(start = X_set[:, 1].min() — 1,
stop = X_set[:, 1].max() + 1, step = 0.01))
plt.contourf(X1, X2, classifier.predict(np.array([X1.ravel(),
X2.ravel()]).T).reshape(X1.shape), alpha = 0.75,
cmap = ListedColormap((‘yellow’, ‘white’, ‘aquamarine’)))
plt.xlim(X1.min(), X1.max())
plt.ylim(X2.min(), X2.max())
for i, j in enumerate(np.unique(y_set)):
plt.scatter(X_set[y_set == j, 0], X_set[y_set == j, 1],
c = ListedColormap((‘red’, ‘green’, ‘blue’))(i), label = j)
plt.title(‘Logistic Regression (Training set)’)
plt.xlabel(‘PC1’) # for Xlabel
plt.ylabel(‘PC2’) # for Ylabel
plt.legend() # to show legend
Step 11: show scatter plot
plt.show()
Step 12: Visualising the Test set results through scatter plot
from matplotlib.colors import ListedColormap
X_set, y_set = X_test, y_test
X1, X2 = np.meshgrid(np.arange(start = X_set[:, 0].min() — 1,
stop = X_set[:, 0].max() + 1, step = 0.01),
np.arange(start = X_set[:, 1].min() — 1,
stop = X_set[:, 1].max() + 1, step = 0.01))
plt.contourf(X1, X2, classifier.predict(np.array([X1.ravel(),
X2.ravel()]).T).reshape(X1.shape), alpha = 0.75,
cmap = ListedColormap((‘yellow’, ‘white’, ‘aquamarine’)))
plt.xlim(X1.min(), X1.max())
plt.ylim(X2.min(), X2.max())
for i, j in enumerate(np.unique(y_set)):
plt.scatter(X_set[y_set == j, 0], X_set[y_set == j, 1],
c = ListedColormap((‘red’, ‘green’, ‘blue’))(i), label = j)
Step 13: title for scatter plot
plt.title(‘Logistic Regression (Test set)’)
plt.xlabel(‘PC1’) # for Xlabel
plt.ylabel(‘PC2’) # for Ylabel
plt.legend()
Step 14: show scatter plot
plt.show()
Neural Network
Simple Neural Network in Python
Step 01:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # to plot error during training
Step 02: input
inputs=np.array([[0,1,0],
[0,1,1], [1,1,0],[1,0,1]])
Step 03: output
outputs=np.array([[0],[0],[1],[1]])
Step 04: create NeuralNetwork class
class NeuralNetwork:
Step 05: intialize variables in class
def __init__(self, inputs, outputs):
self.inputs = inputs
self.outputs = outputs
Step 06: initialize weights as .50 for simplicity
self.weights = np.array([[.50], [.50], [.50]])
self.error_history = []
self.epoch_list = []
Step 07: activation function ==> S(x) = 1/1+e^(-x)
def sigmoid(self, x, deriv=False):
if deriv == True:
return x * (1 — x)
return 1 / (1 + np.exp(-x))
Step 08: data will flow through the neural network.
def feed_forward(self):
self.hidden = self.sigmoid(np.dot(self.inputs, self.weights))
Step 09: going backwards through the network to update weights
def backpropagation(self):
self.error = self.outputs — self.hidden
delta = self.error * self.sigmoid(self.hidden, deriv=True)
self.weights += np.dot(self.inputs.T, delta)
Step 10: train the neural net for 25,000 iterations
def train(self, epochs=25000):
for epoch in range(epochs):
Step 11: flow forward and produce an output
self.feed_forward()
Step 12: go back though the network to make corrections based on the output
self.backpropagation()
Step 13: keep track of the error history over each epoch
self.error_history.append(np.average(np.abs(self.error)))
self.epoch_list.append(epoch)
Step 14: function to predict output on new and unseen input data
def predict(self, new_input):
prediction = self.sigmoid(np.dot(new_input, self.weights))
return prediction
Step 15: create neural network
NN = NeuralNetwork(inputs, outputs)
Step 16: train neural network
NN.train()
Step 17: create two new examples to predict
example = np.array([[1, 1, 0]])
example_2 = np.array([[0, 1, 1]])
Step 18: print the predictions for both examples
print(NN.predict(example), ‘ — Correct: ‘, example[0][0])
print(NN.predict(example_2), ‘ — Correct: ‘, example_2[0][0])
Step 19: plot the error over the entire training duration
plt.figure(figsize=(15,5))
plt.plot(NN.epoch_list, NN.error_history)
plt.xlabel(‘Epoch’)
plt.ylabel(‘Error’)
plt.show()
Handwritten digit recognition (Using Scikit-Learn)
Handwritten digit recognition (Using Scikit-Learn)
Step 001: Loading the Dataset
importing the dataset
from sklearn.datasets import load_digits
digits = load_digits() following command to know the shape of the Dataset:
print(“Image Data Shape” , digits.data.shape)
There are 1797 images in the dataset
Step 002: Visualizing the images and labels in our Dataset
Here we are visualizing the first 5 images in the Dataset
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.figure(figsize=(20,4))
for index, (image, label) in enumerate(zip(digits.data[0:5], digits.target[0:5])):
plt.subplot(1, 5, index + 1)
plt.imshow(np.reshape(image, (8,8)), cmap=plt.cm.gray)
plt.title(‘Training: %i\n’ % label, fontsize = 20)
Step 003: Splitting our Dataset into training and testing sets
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(digits.data, digits.target, test_size=0.05, random_state=95)
Step 004: The Scikit-Learn 4-Step Modeling Pattern
Step 01. Importing the model we want to use.
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
Step 02: Making an instance of the Model
logisticRegr = LogisticRegression()
Step 03: Training the Model
logisticRegr.fit(x_train, y_train)
Step 04. Predicting the labels of new data
predictions = logisticRegr.predict(x_test)
Step 05: Measuring the performance of our Model
Use accuracy_score
score = logisticRegr.score(x_test, y_test)
print(score)
Step 06: Confusion matrix
Using Seaborn for our confusion matrix.
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
from sklearn import metrics
cm = metrics.confusion_matrix(y_test, predictions)
plt.figure(figsize=(9,9))
sns.heatmap(cm, annot=True, fmt=”.3f”, linewidths=.5, square = True, cmap = ‘Pastel1’);
plt.ylabel(‘Actual label’);
plt.xlabel(‘Predicted label’);
all_sample_title = ‘Accuracy Score: {0}’.format(score)
plt.title(all_sample_title, size = 15);
Friendship
Friendship is the most beautiful relation in the world. Friendship is peace, friendship does not have any restrictions of time and space. Th...
-
Identify Overfitting Machine Learning Models In Scikit-Learn STEP 01 To evaluate decision tree performance on train and test sets with dif...
-
Implement multiple linear regression techniques on the Boston house pricing dataset using Scikit-learn. import matplotlib.pyplot as plt impo...
-
Implement multiple linear regression techniques on the Boston house pricing dataset using Scikit-learn.